The State Pension explained
Free money? The State Pension? Some people don’t even know it’s a thing. In this explainer, we unpack the basics to the free pension top-up you’re entitled to throughout retirement. How much will I receive? Is everyone entitled to it? Do I have to claim it when the time comes to retire? These are the answers you’ve been looking for.

You might have a workplace pension - Auto-enrolled, in the background, easy. Maybe you have a personal pension on top of that. But did you know that there’s another kind?
00:14
The State Pension is different and works in addition to the others – it’s like a top-up designed to supplement the money you’ve put aside throughout your working life. The more the merrier, we say. To be eligible, you must have made enough qualifying National Insurance contributions or credits, and the full amount you could receive is £203.85 per week.
00:38
WHO CAN GET IT?
Everyone is entitled to the State Pension, but the amount that you get is based on how many years you’ve paid or been credited with qualifying National Insurance contributions. You know that deduction you usually see on your pay slip? Typically, you need 35 qualifying years to get the full amount.
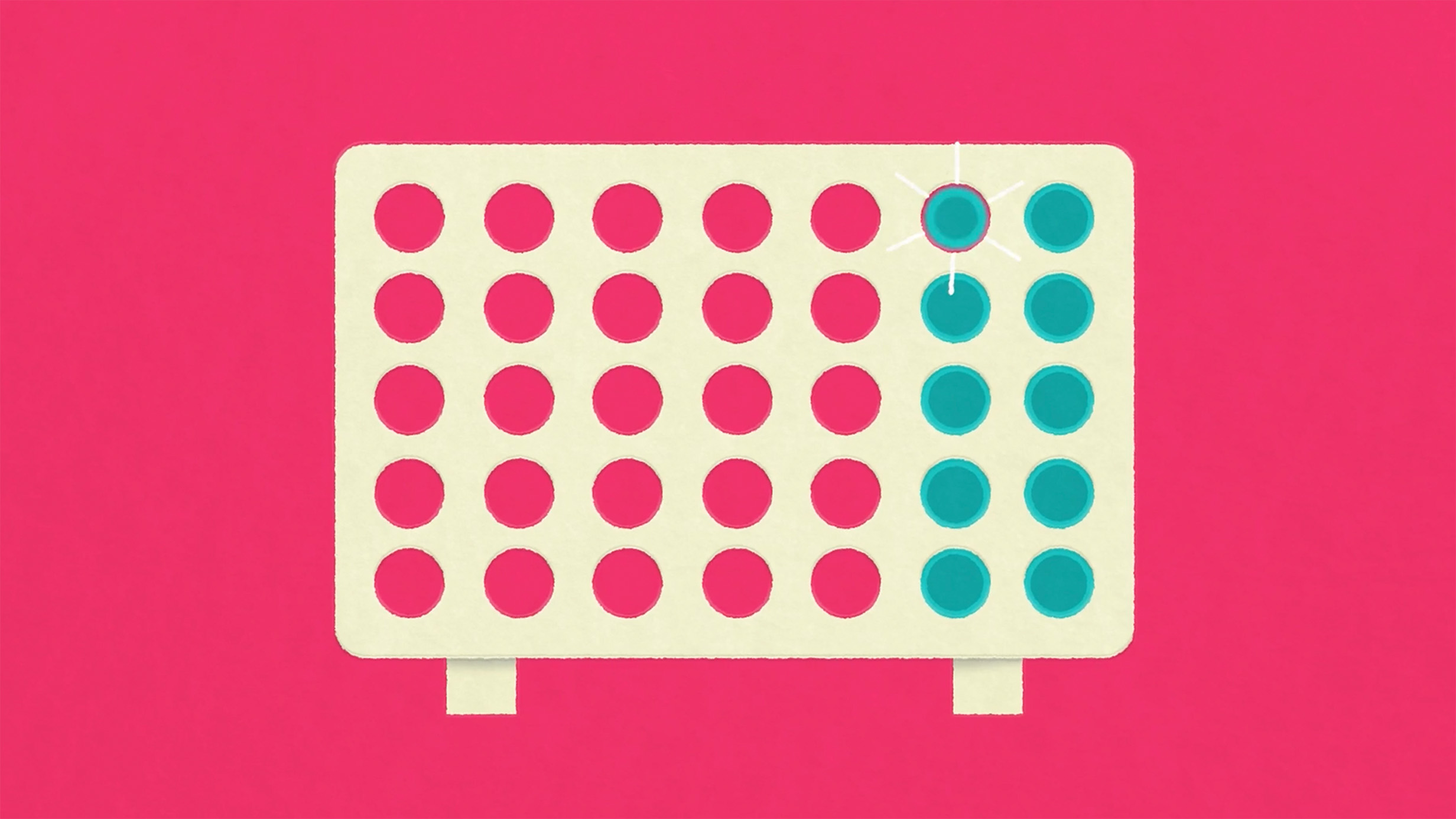
To get any State Pension at all, you need to have made or been credited with a minimum of 10 years of qualifying National Insurance contributions. If you’re a forward-planning-aficionado, a State Pension forecast will give you an idea of how much you’re likely to receive.
01:16
WHEN CAN I GET IT?
The State Pension comes wrapped up with the State Pension Age, which is different for everyone. Currently it’s 66, but it is gradually rising. You can check your State Pension Age on the government’s website. Your age also affects the kind of State Pension you get. There are two main types: New, or Basic.
01:44
 ANYTHING ELSE I NEED TO KNOW?
ANYTHING ELSE I NEED TO KNOW?
You don’t need to retire once you reach State Pension age – you can keep working and receive the State Pension, or you could defer it – just bear in mind that the State Pension you receive is treated as income, so it is taxable. Once you’ve reached State Pension age, you no longer have to pay National Insurance contributions, unless you’re self-employed and pay Class 4 NI contributions.




